Set up and manage Unity Catalog
This article explains how to configure and use Unity Catalog to manage data in your Databricks workspace. It is intended primarily for workspace admins who are using Unity Catalog for the first time. To set up Unity Catalog using the Databricks Terraform provider, see Automate Unity Catalog setup using Terraform.
By the end of this article you will have:
A workspace that is enabled for Unity Catalog.
Compute that has access to Unity Catalog.
Users with permission to access and create objects in Unity Catalog.
You may also want to review other introductory articles:
For a quick walkthrough of how to create a table and grant permissions in Unity Catalog, see Tutorial: Create your first table and grant privileges.
For key Unity Catalog concepts and an introduction to how Unity Catalog works, see What is Unity Catalog?.
To learn how best to use Unity Catalog to meet your data governance needs, see Unity Catalog best practices.
Overview of Unity Catalog enablement
To use Unity Catalog, your Databricks workspaces must be enabled for Unity Catalog, which means that the workspaces are attached to a Unity Catalog metastore, the top-level container for Unity Catalog metadata.
The way admins set up Unity Catalog depends on whether the workspace was enabled automatically for Unity Catalog or requires manual enablement.
Automatic enablement of Unity Catalog
Databricks began to enable new workspaces for Unity Catalog automatically on March 6, 2024, with a rollout proceeding gradually across accounts. Workspaces that were enabled automatically have the following properties:
An automatically-provisioned Unity Catalog metastore (unless a Unity Catalog metastore already existed for the workspace region and the metastore is enabled for automatic workspace assignment).
Default privileges for workspace admins, such as the ability to create a catalog or an external database connection.
No metastore admin (unless an existing Unity Catalog metastore was used and a metastore admin was already assigned).
No metastore-level storage for managed tables and managed volumes (unless an existing Unity Catalog metastore with metastore-level storage was used).
A workspace catalog, which, when originally provisioned, is named after your workspace.
All users in your workspace can create assets in the
defaultschema in this catalog. By default, this catalog is bound to your workspace, which means that it can only be accessed through your workspace. Automatic provisioning of the workspace catalog at workspace creation is rolling out gradually across accounts.
These default configurations will work well for most workspaces, but they can all be modified by a workspace admin or account admin. For example, an account admin can assign a metastore admin and create metastore-level storage, and a workspace admin can modify the workspace catalog name and access.
What if my workspace wasn’t enabled for Unity Catalog automatically?
If your workspace was not enabled for Unity Catalog automatically, an account admin or metastore admin must manually attach the workspace to a Unity Catalog metastore in the same region. If no Unity Catalog metastore exists in the region, an account admin must create one. For instructions, see Create a Unity Catalog metastore.
How do I know if my workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog?
To confirm if your workspace is enabled for Unity Catalog, ask a Databricks workspace admin or account admin to check for you. See also Step 1: Confirm that your workspace is enabled for Unity Catalog.
How do I know if my workspace includes a workspace catalog?
Some new workspaces have a workspace catalog, which, when originally provisioned, is named after your workspace. To determine if your workspace has one, click ![]() Catalog in the sidebar to open Catalog Explorer, and search for a catalog that uses your workspace name as the catalog name.
Catalog in the sidebar to open Catalog Explorer, and search for a catalog that uses your workspace name as the catalog name.
Note
The workspace catalog is like any other catalog in Unity Catalog: a workspace admin can change its name, change its ownership, or even delete it. However, immediately after the workspace is created, it bears the workspace name
Before you begin
Before you begin the tasks described in this article, you should familiarize yourself with the basic Unity Catalog concepts, including metastores, admin roles, and managed storage. See What is Unity Catalog?.
You should also confirm that you meet the following requirements:
A Databricks workspace on the Premium plan.
The following roles and privileges, which depend on the status of your workspace:
Workspace admin: If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog automatically when it was created, you must be a workspace admin to complete the required tasks.
Account admin: If your workspace is not already enabled for Unity Catalog, an account admin must attach the workspace to the metastore.
If there is no Unity Catalog metastore in the same region as the workspace, an account admin must also create the Unity Catalog metastore.
Instructions for determining whether a metastore exists for your workspace region, along with instructions for creating a metastore, follow in this article.
See Admin privileges in Unity Catalog and Automatic enablement of Unity Catalog.
Step 1: Confirm that your workspace is enabled for Unity Catalog
In this step, you determine whether your workspace is already enabled for Unity Catalog, where enablement is defined as having a Unity Catalog metastore attached to the workspace. If your workspace is not enabled for Unity Catalog, you must enable your workspace for Unity Catalog manually. See Next steps if your workspace is not enabled for Unity Catalog.
To confirm, do one of the following.
Use the account console to confirm Unity Catalog enablement
As a Databricks account admin, log into the account console.
Click
 Workspaces.
Workspaces.Find your workspace and check the Metastore column. If a metastore name is present, your workspace is attached to a Unity Catalog metastore and therefore enabled for Unity Catalog.
Run a SQL query to confirm Unity Catalog enablement
Run the following SQL query in the SQL query editor or a notebook that is attached to a cluster that uses shared or single user access mode. See Access modes. No admin role is required.
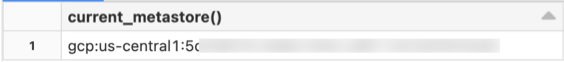
SELECT CURRENT_METASTORE();
If the query returns a metastore ID like the following, then your workspace is attached to a Unity Catalog metastore and therefore enabled for Unity Catalog.
Next steps if your workspace is not enabled for Unity Catalog
If your workspace is not enabled for Unity Catalog (attached to a metastore), the next step depends on whether or not you already have a Unity Catalog metastore defined for your workspace region:
If your account already has a Unity Catalog metastore defined for your workspace region, you can simply attach your workspace to the existing metastore. Go to Enable your workspace for Unity Catalog.
If there is no Unity Catalog metastore defined for your workspace’s region, you must create a metastore and then attach the workspace. Go to Create a Unity Catalog metastore.
When your workspace is enabled for Unity Catalog, go to the next step.
Step 2: Add users and assign the workspace admin role
The user who creates the workspace is automatically added as a workspace user with the workspace admin role (that is, a user in the admins workspace-local group). As a workspace admin, you can add and invite users to the workspace, can assign the workspace admin role to other users, and can create service principals and groups.
Account admins also have the ability to add users, service principals, and groups to your workspace. They can grant the account admin and metastore admin roles.
For details, see Manage users.
(Recommended) Sync account-level identities from your IdP
It can be convenient to manage user access to Databricks by setting up provisioning from a third-party identity provider (IdP), like Okta. For complete instructions, see Sync users and groups from your identity provider.
Step 3: Create clusters or SQL warehouses that users can use to run queries and create objects
To run Unity Catalog workloads, compute resources must comply with certain security requirements. Non-compliant compute resources cannot access data or other objects in Unity Catalog. SQL warehouses always comply with Unity Catalog requirements, but some cluster access modes do not. See Access modes.
As a workspace admin, you can opt to make compute creation restricted to admins or let users create their own SQL warehouses and clusters. You can also create cluster policies that enable users to create their own clusters, using Unity Catalog-compliant specifications that you enforce. See Compute permissions and Create and manage compute policies.
Step 4: Grant privileges to users
To create objects and access them in Unity Catalog catalogs and schemas, a user must have permission to do so. This section describes the user and admin privileges granted on some workspaces by default and describes how to grant additional privileges.
Default user privileges
Some workspaces have default user (non-admin) privileges upon launch:
If your workspace launched with an automatically-provisioned workspace catalog, all workspace users can create objects in the workspace catalog’s
defaultschema.To learn how to determine whether your workspace has a workspace catalog, see How do I know if my workspace includes a workspace catalog?.
If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog manually, it has a
maincatalog provisioned automatically.Workspace users have the
USE CATALOGprivilege on themaincatalog, which doesn’t grant the ability to create or select from any objects in the catalog, but is a prerequisite for working with any objects in the catalog. The user who created the metastore owns themaincatalog by default and can both transfer ownership and grant access to other users.If metastore storage is added after the metastore is created, no
maincatalog is provisioned.
Other workspaces have no catalogs created by default and no non-admin user privileges enabled by default. A workspace admin must create the first catalog and grant users access to it and the objects in it. Skip ahead to Step 5: Create new catalogs and schemas before you complete the steps in this section.
Default admin privileges
Some workspaces have default workspace admin privileges upon launch:
If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog automatically:
Workspace admins can create new catalogs and objects in new catalogs, and grant access to them.
There is no metastore admin by default.
Workspace admins own the workspace catalog (if there is one) and can grant access to that catalog and any objects in that catalog.
If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog manually:
Workspace admins have no special Unity Catalog privileges by default.
Metastore admins must exist and can create any Unity Catalog object and can take ownership of any Unity Catalog object.
For a list of additional object privileges granted to workspace admins in automatically-enabled Unity Catalog workspaces, see Workspace admin privileges when workspaces are enabled for Unity Catalog automatically.
Grant privileges
For access to objects other than those listed in the previous sections, a privileged user must grant that access.
For example, to grant a group the ability to create new schemas in my-catalog, the catalog owner can run the following in the SQL Editor or a notebook:
GRANT CREATE SCHEMA ON my-catalog TO `data-consumers`;
If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog automatically, the workspace admin owns the workspace catalog and can grant the ability to create new schemas:
GRANT CREATE SCHEMA ON <workspace-catalog> TO `data-consumers`;
You can also grant and revoke privileges using Catalog Explorer.
Important
You cannot grant privileges to the workspace-local users or admins groups. To grant privileges on groups, they must be account-level groups.
For details about managing privileges in Unity Catalog, see Manage privileges in Unity Catalog.
Step 5: Create new catalogs and schemas
To start using Unity Catalog, you must have at least one catalog defined. Catalogs are the primary unit of data isolation and organization in Unity Catalog. All schemas and tables live in catalogs, as do volumes, views, and models.
Some workspaces have no automatically-provisioned catalog. To use Unity Catalog, a workspace admin must create the first catalog for such workspaces.
Other workspaces have access to a pre-provisioned catalog that your users can access to get started (either the workspace catalog or the main catalog, depending on how your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog). As you add more data and AI assets into Databricks, you can create additional catalogs to group those assets in a way that makes it easy to govern data logically.
For recommendations about how best to use catalogs and schemas to organize your data and AI assets, see Unity Catalog best practices.
As a metastore admin, workspace admin (auto-enabled workspaces only), or other user with the CREATE CATALOG privilege, you can create new catalogs in the metastore. When you do, you should:
Create managed storage for the new catalog.
Managed storage is a dedicated storage location in your Google Cloud account for managed tables and managed volumes. You can assign managed storage to the metastore, to catalogs, and to schemas. When a user creates a table, the data is stored in the storage location that is lowest in the hierarchy. For example, if a storage location is defined for the metastore and catalog but not the schema, the data is stored in the location defined for the catalog.
Databricks recommends that you assign managed storage at the catalog level, because catalogs typically represent logical units of data isolation. If you are comfortable with data in multiple catalogs sharing the same storage location, you can default to the metastore-level storage location. If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog automatically, there is no metastore-level storage by default. An account admin has the option to configure metastore-level storage. See Specify a managed storage location in Unity Catalog and Add managed storage to an existing metastore.
Assigning managed storage to a catalog requires that you create:
A storage credential.
An external location that references that storage credential.
For an introduction to these objects and instructions for creating them, see Connect to cloud object storage using Unity Catalog.
Bind the new catalog to your workspace if you want to limit access from other workspaces that share the same metastore.
Grant privileges on the catalog.
For detailed instructions, see Create catalogs.
Catalog creation example
The following example shows the creation of a catalog with managed storage, followed by granting the SELECT privilege on the catalog:
CREATE CATALOG IF NOT EXISTS mycatalog
MANAGED LOCATION 'gs://depts/finance';
GRANT SELECT ON mycatalog TO `finance-team`;
For more examples, including instructions for creating catalogs using Catalog Explorer, see Create catalogs.
Create a schema
Schemas represent more granular groupings (like departments or projects, for example) than catalogs. All tables and other Unity Catalog objects in the catalog are contained in schemas. As the owner of a new catalog, you may want to create the schemas in the catalog. But you might want instead to delegate the ability to create schemas to other users, by giving them the CREATE SCHEMA privilege on the catalog.
For detailed instructions, see Create schemas.
(Optional) Assign the metastore admin role
If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog automatically, no metastore admin role is assigned by default. Metastore admins have some privileges that workspace admins don’t.
You might want to assign a metastore admin if you need to:
Change ownership of catalogs after someone leaves the company.
Manage and delegate permissions on the init script and jar allowlist.
Delegate the ability to create catalogs and other top-level permissions to non-workspace admins.
Receive shared data through Delta Sharing.
Add managed storage to the metastore, if it has none. See Add managed storage to an existing metastore.
For detailed information about the metastore admin role and instructions for assigning it, see Assign a metastore admin.
Upgrade tables in your Hive metastore to Unity Catalog tables
If your workspace was in service before it was enabled for Unity Catalog, it likely has a Hive metastore that contains data that you want to continue to use. Databricks recommends that you migrate the tables managed by the Hive metastore to the Unity Catalog metastore.
(Optional) Keep working with your Hive metastore
If your workspace has a Hive metastore that contains data that you want to continue to use, and you choose not to follow the recommendation to upgrade the tables managed by the Hive metastore to the Unity Catalog metastore, you can continue to work with data in the Hive metastore alongside data in the Unity Catalog metastore.
The Hive metastore is represented in Unity Catalog interfaces as a catalog named hive_metastore. In order to continue working with data in your Hive metastore without having to update queries to specify the hive_metastore catalog, you can set the workspace’s default catalog to hive_metastore. See Manage the default catalog.
Depending on when your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog, the default catalog may already be hive_metastore.
(Optional) Create metastore-level storage
Although Databricks recommends that you create a separate managed storage location for each catalog in your metastore (and you can do the same for schemas), you can opt instead to create a managed location at the metastore level and use it as the storage for multiple catalogs and schemas.
If you want metastore-level storage, you must also assign a metastore admin. See (Optional) Assign the metastore admin role.
Metastore-level storage is required only if you use a Databricks partner product integration that relies on personal staging locations (deprecated).
For more information about the hierarchy of managed storage locations, see Data is physically separated in storage.
To learn how to add metastore-level storage to metastores that have none, see Add managed storage to an existing metastore.
Note
Most workspaces that were enabled for Unity Catalog before March 6, 2024 have a metastore-level storage root.
Next steps
Run a quick tutorial to create your first table in Unity Catalog: Tutorial: Create your first table and grant privileges
Learn more about Unity Catalog: What is Unity Catalog?
Learn best practices for using Unity Catalog: Unity Catalog best practices
Learn how to grant and revoke privileges: Manage privileges in Unity Catalog
Install the Databricks CLI: What is the Databricks CLI?