Share code between Databricks notebooks
This article describes how to use files to modularize your code, including how to create and import Python files.
Databricks also supports multi-task jobs which allow you to combine notebooks into workflows with complex dependencies. For more information, see Overview of orchestration on Databricks.
Modularize your code using files
With Databricks Runtime 11.3 LTS and above, you can create and manage source code files in the Databricks workspace, and then import these files into your notebooks as needed. You can also use a Databricks repo to sync your files with a Git repository. For details, see Work with Python and R modules and Git integration for Databricks Git folders.
Create a file
To create a file:
Right-click on the folder name and select Create > File.
Enter a name for the file and click Create File or press Enter. The file opens in an editor window. Changes are saved automatically.
Open a file
Navigate to the file in your workspace and click on it. The file path displays when you hover over the name of the file.
Import a file into a notebook
You can import a file into a notebook using standard Python import commands:
Suppose you have the following file:
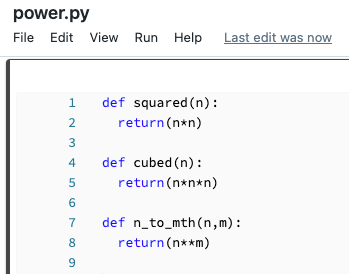
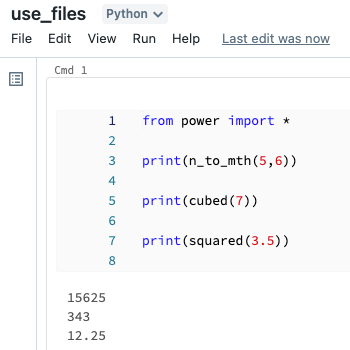
You can import that file into a notebook and call the functions defined in the file:
Run a file
You can run a file from the editor. This is useful for testing. To run a file, place your cursor in the code area and select Shift + Enter to run the cell, or highlight code in the cell and press Shift + Ctrl + Enter to run only the selected code.
Delete a file
See Folders and Workspace object operations for information about how to access the workspace menu and delete files or other items in the workspace.
Rename a file
To change the title of an open file, click the title and edit inline or click File > Rename.
Control access to a file
If your Databricks account has the Premium plan, you can use Workspace access control to control who has access to a file.