Enable and try Databricks Assistant
Databricks Assistant is a context-aware AI assistant that helps you with Databricks notebooks, SQL editor, jobs, AI/BI dashboards, and file editor. Databricks Assistant assists you with data and code when you ask for help using a conversational interface.
To learn how Assistant helps with code, see Get coding help from Databricks Assistant.
For an account: Disable or enable Databricks Assistant features
Tip
If you can’t enable Databricks Assistant using the following instructions, you might need to disable Enforce data processing within workspace Geography for AI features. See Enable cross-Geo processing.
Partner-powered Databricks Assistant features are enabled by default. However, account admins can disable Partner-powered Assistant features for all workspaces within an account. Account admins can also enforce enabling Databricks Assistant for the entire account:
Tip
The act of enabling or disabling Partner-powered Databricks Assistant features for your account is captured as an account event in your audit logs, see Account events.
As an account admin, log in to the account console.
Click Settings.
Click the Feature enablement tab.
For the Enable partner-powered AI features option, select Off or On.
Prevent workspace overrides with the Enforce setting:

To learn about the services used for Partner-powered Databricks Assistant features, see Features governed by the **Partner-powered AI assistive features** setting.
For a workspace: Disable or enable Assistant features
If your account admin enables Assistant, it is enabled by default in workspaces. Unless the account admin chose to enforce the setting, workspace admins can disable it for their workspaces.
To disable Databricks Assistant in a workspace:
Click your username in the top bar of the Databricks workspace > Settings.
In the left pane under Workspace admin, click the Advanced tab.
To disable Assistant, click the toggle Off for AI-powered AI assistive features.
Disable or enable Databricks Assistant completely
To disable Databricks Assistant completely:
Admins: Follow instructions to disable or enable Databricks Assistant features for an account.
Workspace admins: Follow instructions to disable or enable Assistant features for a workspace.
If you turn off only the Enable Partner-powered AI assitive features option, Databricks-hosted models continue to power the following:
Autocomplete
Unity Catalog data comments
Quickfix suggestions
Tour of the Assistant pane
This section describes the default experience of the Assistant pane.
To open the Assistant pane, click ![]() in the left sidebar.
in the left sidebar.

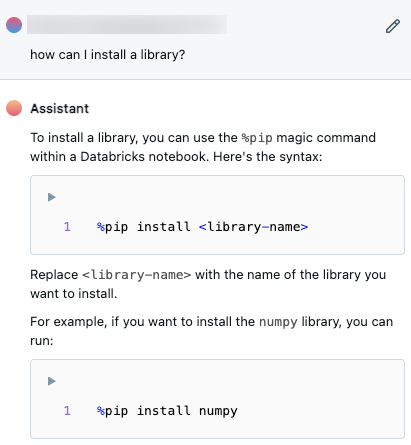
Type questions in the text box at the bottom of the Assistant pane and press Enter or click  at the right of the text box. Assistant displays its answer. The following screenshot shows actions you can take after Assistant has generated code in the Assistant pane.
at the right of the text box. Assistant displays its answer. The following screenshot shows actions you can take after Assistant has generated code in the Assistant pane.

You can run the same query again to generate another answer. To do so, hover your cursor over the answer and click  .
.
To close the pane, click the icon again or click  in the upper-right corner of the cell. You can expand the pane to full width by clicking
in the upper-right corner of the cell. You can expand the pane to full width by clicking  ; click
; click ![]() to return the pane to default width.
to return the pane to default width.
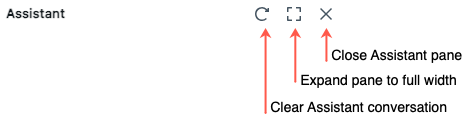
The Assistant pane keeps track of your conversations even if you close the pane or notebook. To clear previous conversations, click ![]() at the upper-right of the Assistant pane.
at the upper-right of the Assistant pane.
Threads and prompt history
Conversation threads persist across the different contexts where Databricks Assistant is available. From the Assistant pane, you can create new conversation threads, view the question and prompt history, and manage your Databricks Assistant experience.

Databricks Assistant titles the threads based on the context of your prompts, so you can navigate the history of your Assistant conversation. The following example is from a question about a notebook.

Get help with code
Get help with code from Databricks Assistant directly in your notebooks. The Assistant offers:
Data filtering with natural language prompts.
Code debugging with Diagnose Error.
Quick Fix, which presents automatic recommendations for fixing code errors that you can Accept and run.
Get answers from Databricks documentation
In the notebook editor, Databricks Assistant can answer questions based on Databricks documentation. Type your question or prompt into the prompt box.