Serverless compute for notebooks
Preview
This feature is in Public Preview.
This article explains how to use serverless compute for notebooks. For information on using serverless compute for jobs, see Run your Databricks job with serverless compute for workflows.
For pricing information, see Databricks pricing.
Requirements
Your workspace must be enabled for Unity Catalog.
Your workspace must be in a supported region. See Databricks clouds and regions.
Your account must be enabled for serverless compute. See Enable serverless compute.
Attach a notebook to serverless compute
If your workspace is enabled for serverless interactive compute, all users in the workspace have access to serverless compute for notebooks. No additional permissions are required.
To attach to the serverless compute, click the Connect drop-down menu in the notebook and select Serverless. For new notebooks, the attached compute automatically defaults to serverless upon code execution if no other resource has been selected.
View query insights
Serverless compute for notebooks and jobs uses query insights to assess Spark execution performance. After running a cell in a notebook, you can view insights related to SQL and Python queries by clicking the See performance link.
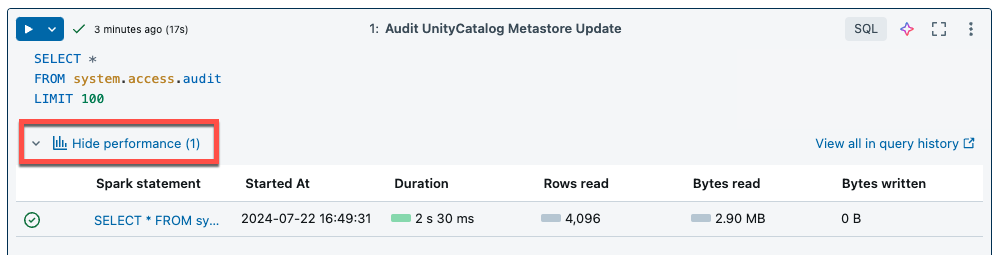
You can click on any of the Spark statements to view the query metrics. From there you can click See query profile to see a visualization of the query execution. For more information on query profiles, see Query profile.
Note
To view performance insights for your job runs, see View job run query insights.
Query history
All queries that are run on serverless compute will also be recorded on your workspace’s query history page. For information on query history, see Query history.
Query insight limitations
The query profile is only available after the query execution terminates.
Metrics are updated live although the query profile is not shown during execution.
Only the following query statuses are covered: RUNNING, CANCELED, FAILED, FINISHED.
Running queries cannot be canceled from the query history page. They can be canceled in notebooks or jobs.
Verbose metrics are not available.
Query Profile download is not available.
Access to the Spark UI is not available.
The statement text only contains the last line that was run. However, there might be several lines preceding this line that were run as part of the same statement.
Which regions support serverless compute?
Serverless compute for notebooks and serverless compute for workflows are supported in the following regions:
us-central1us-east1
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
How are releases rolled out?
Serverless compute is a versionless product, which means that Databricks automatically upgrades the serverless compute runtime to support enhancements and upgrades to the platform. All users get the same updates, rolled out over a short period of time.
How do I determine which serverless version I am running?
Serverless workloads always run on the latest runtime version. See Release notes for the most recent version.
How do I estimate costs for serverless?
Databricks recommends running and benchmarking a representative or specific workload and then analyzing the billing system table. See Billable usage system table reference.
How do I analyze DBU usage for a specific workload?
To see the cost for a specific workload, query the system.billing.usage system table. See Monitor the cost of serverless compute for sample queries and to download our cost observability dashboard.
Does serverless compute support private repos?
Repositories can be private or require authentication. For security reasons, a pre-signed URL is required when accessing authenticated repositories.
How do I install libraries for my job tasks?
Databricks recommends using environments to install and manage libraries for your jobs. See Configure environments and dependencies for non-notebook tasks.
Can I connect to custom data sources?
No, only the sources using Lakehouse Federation are supported. See Supported data sources.
How does the serverless compute plane networking work?
Serverless compute resources run in the serverless compute plane, which is managed by Databricks. For more details on the network and architecture, see Serverless compute plane networking.