Manage users, service principals, and groups
This article introduces the Databricks identity management model and provides an overview of how to manage users, groups, and service principals in Databricks.
For an opinionated perspective on how to best configure identity in Databricks, see Identity best practices.
To manage access for users, service principals, and groups, see Authentication and access control.
Databricks identities
There are three types of Databricks identity:
Users: User identities recognized by Databricks and represented by email addresses.
Service principals: Identities for use with jobs, automated tools, and systems such as scripts, apps, and CI/CD platforms.
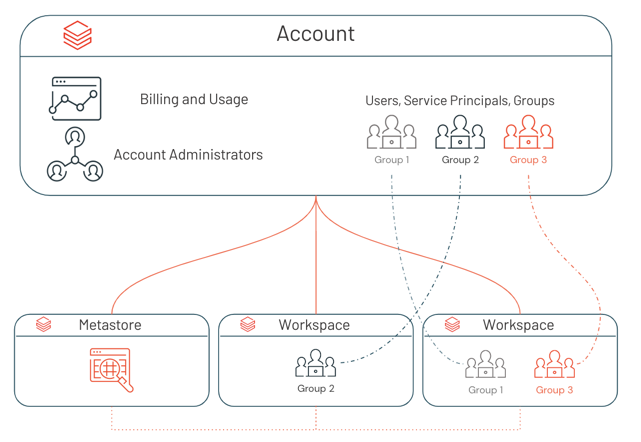
Groups: A collection of identities used by admins to manage group access to workspaces, data, and other securable objects. All Databricks identities can be assigned as members of groups. There are two types of groups in Databricks: account groups and workspace-local groups. For more information, see Types of groups in Databricks.
A Databricks account can have a maximum of 10,000 combined users and service principals, along with up to 5,000 groups. Each workspace also can have a maximum of 10,000 combined users and service principals as members, along with up to 5,000 groups.
For detailed instructions, see:
Who can manage identities in Databricks?
To manage identities in Databricks, you must have one of the following: the account admin role, the workspace admin role, or the manager role on a service principal or group.
Account admins can add users, service principals, and groups to the account and assign them admin roles. Account admins can update and delete users, service principals, and groups in the account. They can give users access to workspaces, as long as those workspaces use identity federation.
Workspace admins can add users and service principals to the Databricks account. They can also add groups to the Databricks account if their workspaces are enabled for identity federation. Workspace admins can grant users, service principals, and groups access to their workspaces. They cannot delete users and service principals from the account.
Workspace admins can also manage workspace-local groups. For more information, see Manage workspace-local groups (legacy).
Group managers can manage group membership and delete the group. They can also assign other users the group manager role. Account admins have the group manager role on all groups in the account. Workspace admins have the group manager role on account groups that they create. See Who can manage account groups?.
Service principal managers can manage roles on a service principal. Account admins have the service principal manager role on all service principals in the account. Workspace admins have the service principal manager role on service principals that they create. For more information, see Roles for managing service principals.
How do admins assign users to the account?
Databricks recommends using SCIM provisioning to sync all users and groups automatically from your identity provider to your Databricks account. Users in a Databricks account do not have any default access to a workspace, data, or compute resources. Account admins and workspace admins can assign account users to workspaces. Workspace admins can also add a new user directly to a workspace, which both automatically adds the user to the account and assigns them to that workspace.
Users can share published dashboards with other users in the Databricks account, even if those users are not members of their workspace. Users in the Databricks account who are not members of any workspace are the equivalent of view-only users in other tools. They can view objects that have been shared with them, but they cannot modify objects. For more information, see User and group management for dashboard sharing.
For detailed instructions on adding users to the account, see:
How do admins assign users to workspaces?
To enable a user, service principal, or group to work in a Databricks workspace, an account admin or workspace admin needs to assign them to a workspace. You can assign workspace access to users, service principals, and groups that exist in the account as long as the workspace is enabled for identity federation.
Workspace admins can also add a new user, service principal, or account group directly to a workspace. This action automatically adds the chosen user, service principal, or account group to the account and assigns them to that particular workspace.
Note
Workspace admins can also create legacy workspace-local groups in workspaces using the Workspace Groups API. Workspace-local groups are not automatically added to the account. Workspace-local groups cannot be assigned to additional workspaces, or granted access to data in a Unity Catalog metastore.
For those workspaces that aren’t enabled for identity federation, workspace admins manage their workspace users, service principals, and groups entirely within the scope of the workspace. Users and service principals added to non-identity federated workspaces are automatically added to the account. Groups added to non-identity federated workspaces are legacy workspace-local groups that are not added to the account.
If the workspace user shares a username (email address) with an account user or admin that already exists, those users are merged.
For detailed instructions, see:
How do admins enable identity federation on a workspace?
Databricks began to enable new workspaces for identity federation and Unity Catalog automatically on March 6, 2024, with a rollout proceeding gradually across accounts. If your workspace is enabled for identity federation by default, it cannot be disabled. For more information, see Automatic enablement of Unity Catalog.
To enable identity federation in a workspace, an account admin needs to enable the workspace for Unity Catalog by assigning a Unity Catalog metastore. See Enable a workspace for Unity Catalog.
When the assignment is complete, identity federation is marked as Enabled on the workspace’s Configuration tab in the account console.
Workspace admins can tell if a workspace has identity federation enabled from the workspace admin settings page. In an identity federated workspace, when you choose to add a user, service principal, or group in workspace admin settings, you have the option to select a user, service principal, or group from your account to add to the workspace.
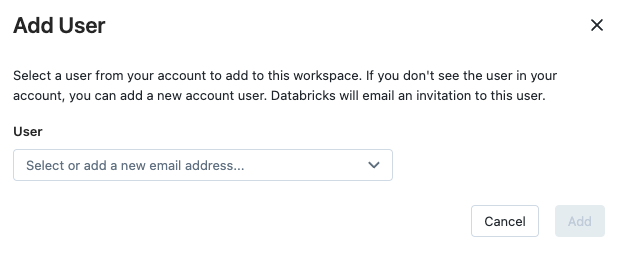
In a non-identity federated workspace, you do not have the option to add users, service principals, or groups from your account.
Assigning admin roles
Account admins can assign other users as account admins. They can also become Unity Catalog metastore admins by virtue of creating a metastore, and they can transfer the metastore admin role to another user or group.
Both account admins and workspace admins can assign other users as workspace admins. The workspace admin role is determined by membership in the workspace admins group, which is a default group in Databricks and cannot be deleted.
Account admins can also assign other users as Marketplace admins.
See:
Setting up single sign-on (SSO)
Databricks account and workspace users authenticate with their Google Cloud Identity account (or GSuite account) using Google’s OAuth 2.0 implementation, which conforms to the OpenID Connect spec and is OpenID certified. Databricks provides the openid profile scope values in the authentication request to Google.
Optionally, you can configure your Google Cloud Identity account (or GSuite account) to federate with an external SAML 2.0 Identity Provider (IdP) to verify user credentials. Google Cloud Identity can federate with Microsoft Entra ID, Okta, Ping, and other IdPs. However, Databricks only interacts directly with the Google Identity Platform APIs.