Credentials
Applies to:  Databricks SQL
Databricks SQL  Databricks Runtime
Databricks Runtime  Unity Catalog only
Unity Catalog only
Unity Catalog and the built-in Databricks Hive metastore use default locations for managed tables. Unity Catalog introduces several new securable objects to grant privileges to external cloud services and data in cloud object storage.
-
A Unity Catalog credential used to access external locations and tables.
-
A Unity Catalog object used to associate a cloud object storage URI with a storage credential.
-
A Unity Catalog table created in a Unity Catalog-managed external location.
Credential
A credential is a securable object representing a Google Cloud service account.
After a credential is created, access to it can be granted to principals (users and groups).
Storage credentials are primarily used to create external locations, which scope access to a specific storage path.
Credential names are unqualified and must be unique within the metastore.
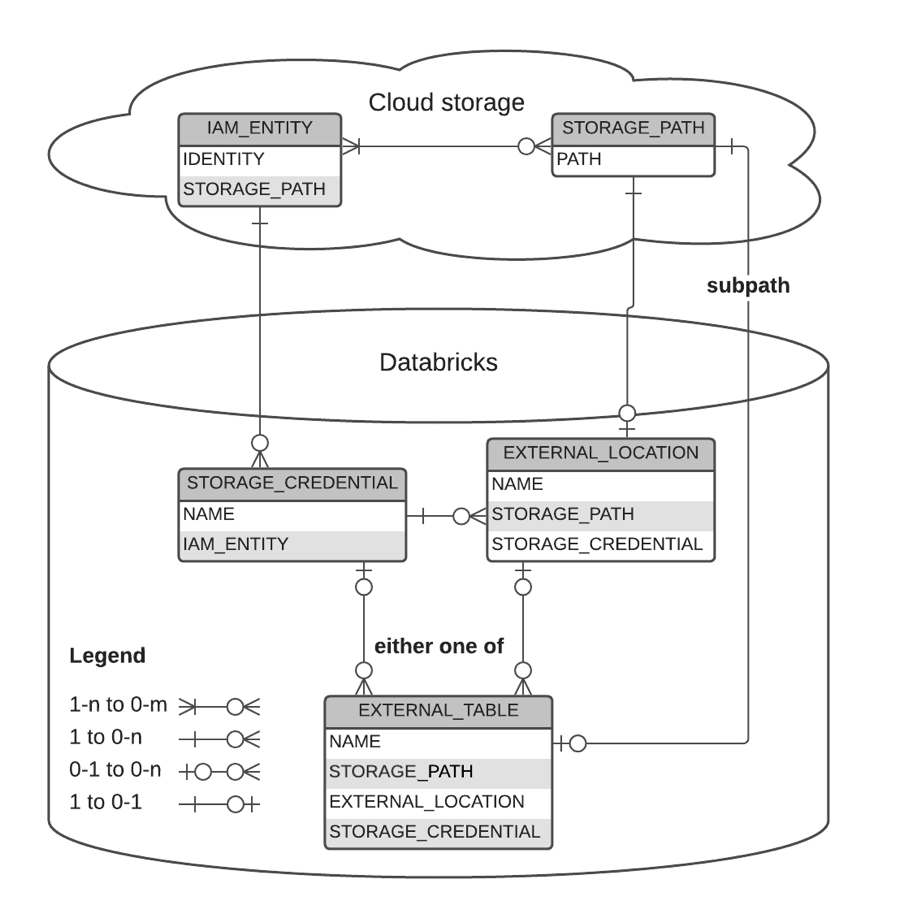
Graphical Representation of relationships
The following diagram describes the relationship between:
storage credentials
external locations
external tables
storage paths
IAM entities
Azure service accounts
Examples
Using CLI create a storage credential my_storage_cred for a Google Cloud service account.
databricks storage-credentials create --json '{"name": "my_storage_cred", "databricks_gcp_service_account": {}}'
The rest of the commands can be run within SQL.
-- Grant access to the storage credential
> GRANT READ FILES ON STORAGE CREDENTIAL my_storage_cred TO ceo;
-- ceo can directly read from any storage path using my_storage_cred
> SELECT count(1) FROM `delta`.`gs://depts/finance/forecast/somefile` WITH (CREDENTIAL my__storage_cred);
100
> SELECT count(1) FROM `delta`.`gs://depts/hr/employees` WITH (CREDENTIAL my__storage_cred);
2017
-- Create an external location on specific path to which `my_storage_cred` has access
> CREATE EXTERNAL LOCATION finance_loc URL 'gs://depts/finance'
WITH (CREDENTIAL my_storage_cred)
COMMENT 'finance';